The family portfolio of the great British artist Thomas Gainsborough (1727–1788) is the most comprehensive collection of personal family portraits by any artist—of his time or of any time prior. Collectively, these portraits are a unique peek into the life of ordinary 18th-century people, in this case a middle-class family, at a time when most portraits could only be afforded by the wealthy.
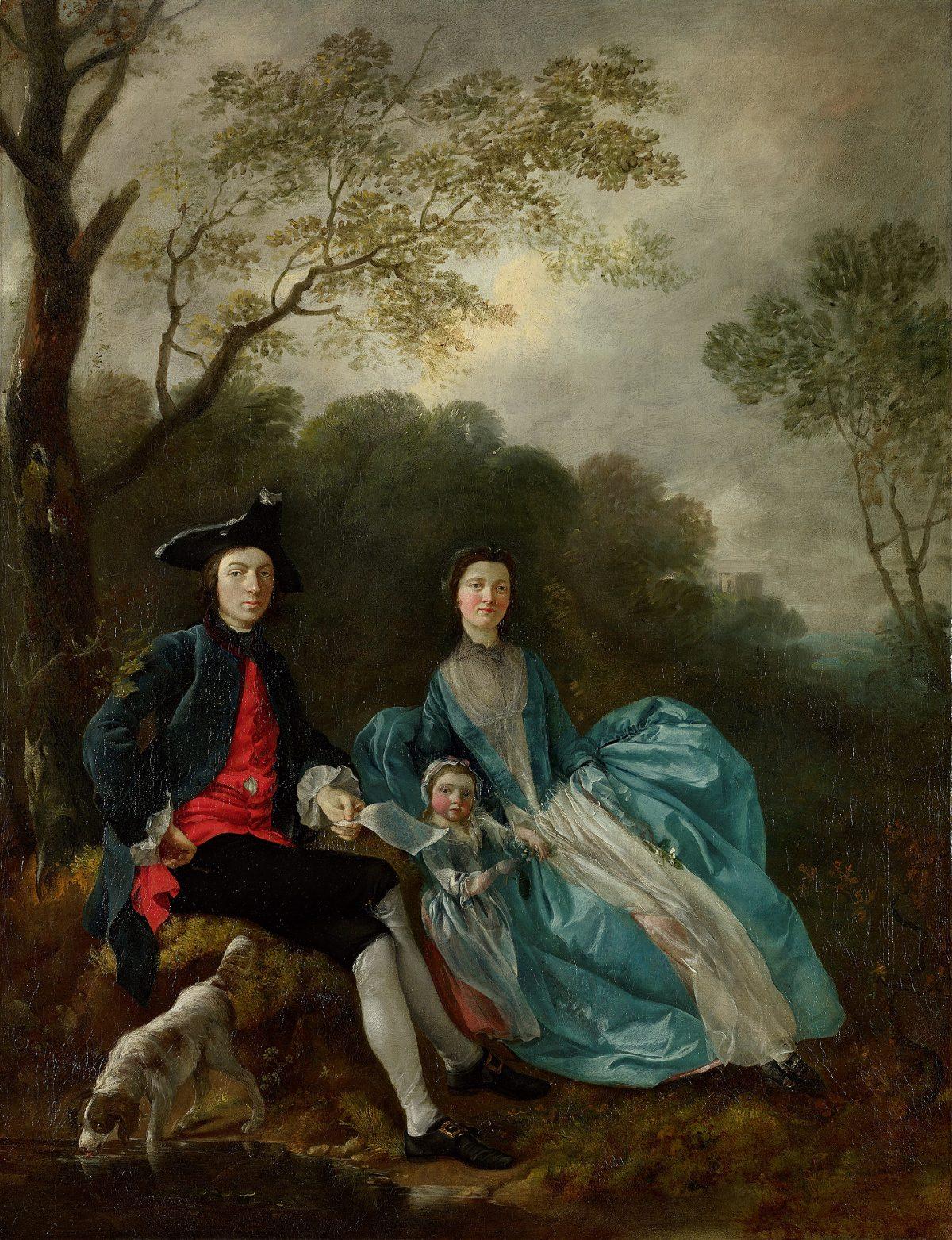

“The Artist with His Wife Margaret and Eldest Daughter Mary,” circa 1748, by Thomas Gainsborough. Oil on canvas. Acquired under the acceptance-in-lieu scheme at the wish of Sybil, Marchioness of Cholmondeley, in memory of her brother, Sir Philip Sassoon, 1994, The National Gallery, London. The National Gallery, London