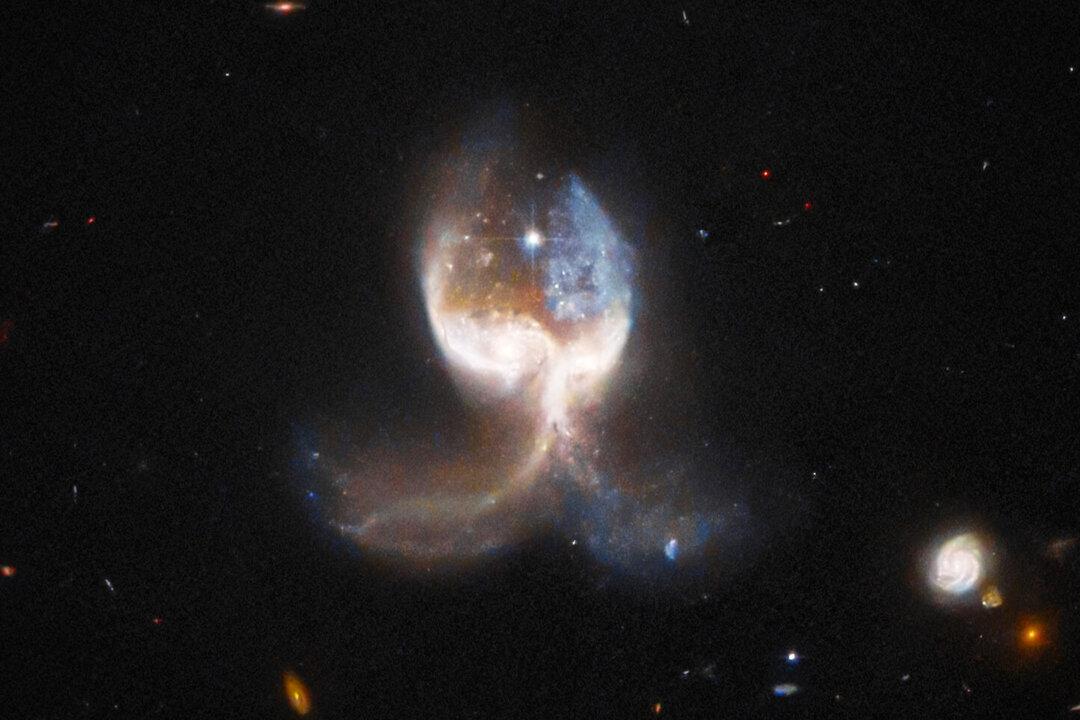
Out of a vast galactic menagerie of space images, a pair of celestial “angel wings” was discovered by researchers—the stunning spectacle, composed of trails of stars and dust, formed as a result of two galaxies colliding.
The picture, taken by NASA/ESA’s Hubble Space Telescope, shows a nearly symmetrical object in the VV689 system, in the constellation Leo, which is actually the product of two distinct galaxies in the process of merging.