In Partnership With Trio Nutrition
Introduction
The diets of many people in the United States provide less than the recommended amounts of magnesium. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), studies reliably show that many Americans consume less than recommended amounts of magnesium. In fact, “48% of Americans of all ages ingest less magnesium from food and beverages than their respective EARS” or Estimated Average Requirements.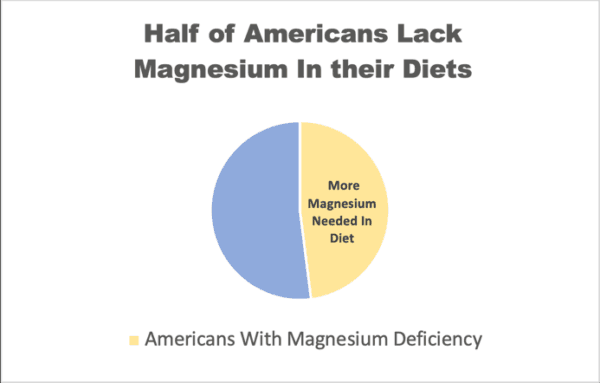
Source: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) of 2013–2016
Magnesium Matters: Vulnerable Populations in the United States
- Elderly Population: Older adults have lower intake of magnesium in their diet than younger adults. Magnesium deficiency in the elderly is further exacerbated by the fact that magnesium absorption from the gut decreases with age.

Trio Nutrition
- Individuals Consuming Excessive Alcohol: In these individuals, a long list of medical conditions can result from consuming excessive alcohol such as liver disease and poor dietary intake including vitamin D deficiency; and, these factors lead to magnesium shortfalls in the body.
- Individuals Suffering from Certain Diseases: Conditions like type 2 diabetes, gastrointestinal disorders, such as Crohn’s disease and celiac disease, and kidney disease can interfere with magnesium absorption into the body or increase the excretion of magnesium from the body.
- Individuals on Certain Medications: Some medications, such as diuretics and proton pump inhibitors, can deplete magnesium levels in the body.
- High Performance Athletes: Some nutritionists believe that physically active individuals may have higher magnesium requirements to maintain optimal exercise performance. As such, athletes are more likely to have a magnesium deficit in their diets compared with their less active peers.
- Individuals with Poor Dietary Regimen: Individuals with diets that are high in processed foods and low in magnesium-rich foods can have Magnesium deficiency.
Why It is Crucial to Prevent Magnesium Deficiency for Your Health
Magnesium is an essential mineral and a nutrient that the body needs to stay healthy. Did you know that an adult body contains approximately 25 g magnesium? And, magnesium is required in hundreds of essential biochemical activities in the human body.Based on studies cited by the NIH, in the short term, when healthy people have low intakes of magnesium in their diet, the kidneys help to retain magnesium by limiting the amount lost in urine. But any prolonged deficit of magnesium in your diet will lead to magnesium deficiency possibly contributing to an array of health issues:
- High blood pressure and heart disease
- Cardiovascular disease and stroke
- Type 2 diabetes
- Bone fractures and osteoporosis
- Migraine headache, stress and poor sleep

Trio Nutrition
Research to date has shown that magnesium deficiency may lead to the above-mentioned health issues but more research is required to gain a better understanding of these issues.
Understanding Your Daily Magnesium Needs: What Are the RDAs?
Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) of Magnesium is defined as the average daily level of intake of Magnesium sufficient to meet the nutrient requirements of healthy individuals. Here are the RDA for Magnesium: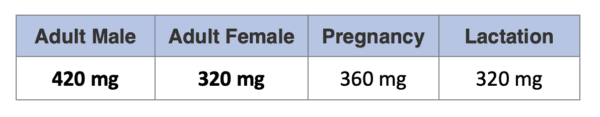
But some nutritionists believe that the demand for magnesium is likely to increase during accelerated metabolic situations for athletes. Thus, physically active individuals may have higher magnesium requirements to maintain optimal exercise performance, as compared with their less active peers but further research is required.

Trio Nutrition
Easy Ways to Add More Magnesium to Your Daily Diet
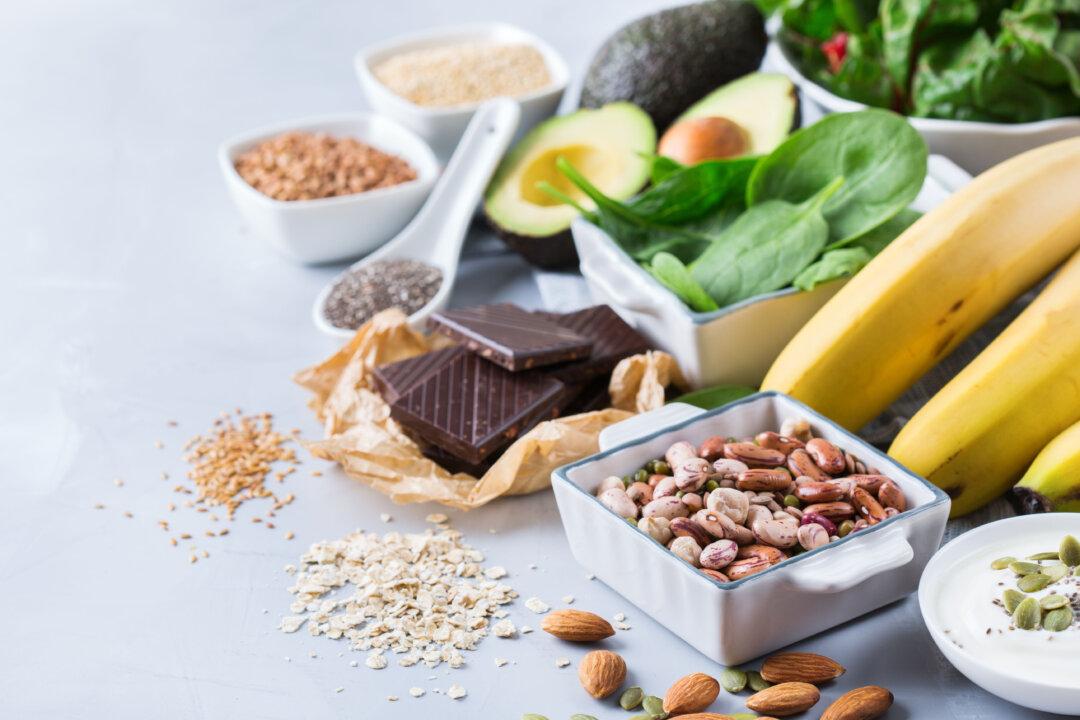
As a good rule, foods containing dietary fiber are a source of magnesium in your diet. Dietary Sources of Magnesium include:- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are excellent sources of magnesium.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, cashews, and pumpkin seeds are rich in magnesium.
- Whole Grains: Foods like whole wheat, brown rice, and oats contain magnesium.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas provide a healthy dose of magnesium.
- Dairy: Some dairy products, like yogurt and milk, are good dietary sources.
- Seafood: Salmon and mackerel are the ocean’s gift to your magnesium intake.
- Magnesium-Rich Water: Some natural spring waters and mineral waters contain magnesium.
- Nutritional Supplements: Magnesium supplements are widely available and can help individuals meet their daily requirements. We recommend trying Trio Nutrition’s World-Famous Magximum and Magnesium Complex.
Is a Magnesium Supplement an Essential Requirement for My Health and Diet?
Generally, only 30% to 40% of the dietary magnesium eaten is typically absorbed by the body. And, given that 48% of Americans of all ages ingest less magnesium from food and beverages, you may want to strongly consider increasing your magnesium consumption by taking a magnesium nutritional supplement.
Trio Nutrition
If you are looking for a magnesium supplement that is easily absorbed, bioavailable and less likely to cause digestive upset, then magnesium glycinate is a good choice and you should try Trio Nutrition’s Magximum. Alternatively, if you are looking for a magnesium supplement that is economical and provides a high dose of magnesium, then magnesium oxide is a good option. In the latter case, Trio Nutrition’s Magnesium Complex, which is a blend of Magnesium Glycinate and Magnesium Oxide, is right for you.
Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance on your supplement choices and dietary needs to achieve optimal health outcomes. A well-balanced diet, along with the right supplements, can pave the way for a healthier and happier you.






