There are plenty of reasons why you may need to take ownership of files and folders in Windows. For one, when you are replacing or modifying a system for some custom edits, you may receive errors stating that you don’t have enough privileges to access that specific file or folder.
In those scenarios, you can simple take ownership of that file of folder as an Administrator. But like many things in Windows, there are several steps involved, and it is sometimes confusing and cumbersome for beginners.
So if you ever need help, here is how you can take ownership of files and folders in Windows so that you can easily edit or modify system files without any “Access denied” errors.
What does Take Ownership Mean?
Technically speaking, most of the system files and folders are locked to prevent themselves from being modified. This is an important security feature to protect system integrity. If you ever need to modify these files for whatever reason, you need to acquire the necessary permission to access and modify the files.
Take Ownership of a File or Folder
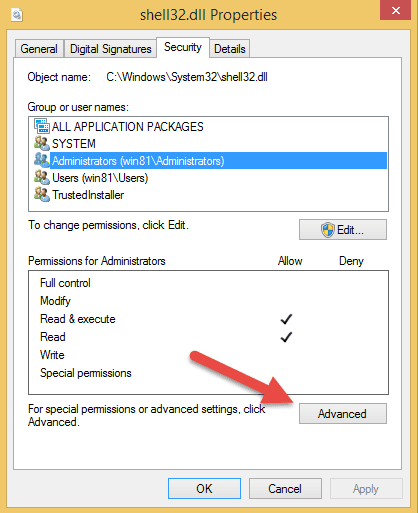
Note: To demonstrate the procedure, I’m taking “shell32.dll” system file as an example which is created by Windows itself. The same procedure is applicable to any file or folder. In case you are wondering, “shell32.dll” is a file which holds most of the Windows shell API functions.
To take ownership of a file or folder, we need to edit some of the properties of the said file or folder. To do that, right click on a file and select the option “Properties.” This action will open the file properties window. Here navigate to the “Security” tab and click on the “Advanced” button located at the bottom of the window to open “Advanced Security Settings”.