Since early 2021, the Beta Cell Foundation has collected data on vaccine adverse events from 528 patients with type 1 diabetes by using an online database for analysis.
The analysis showed that some patients with type 1 diabetes experienced elevated (or disturbed) blood glucose levels after vaccination with COVID vaccines: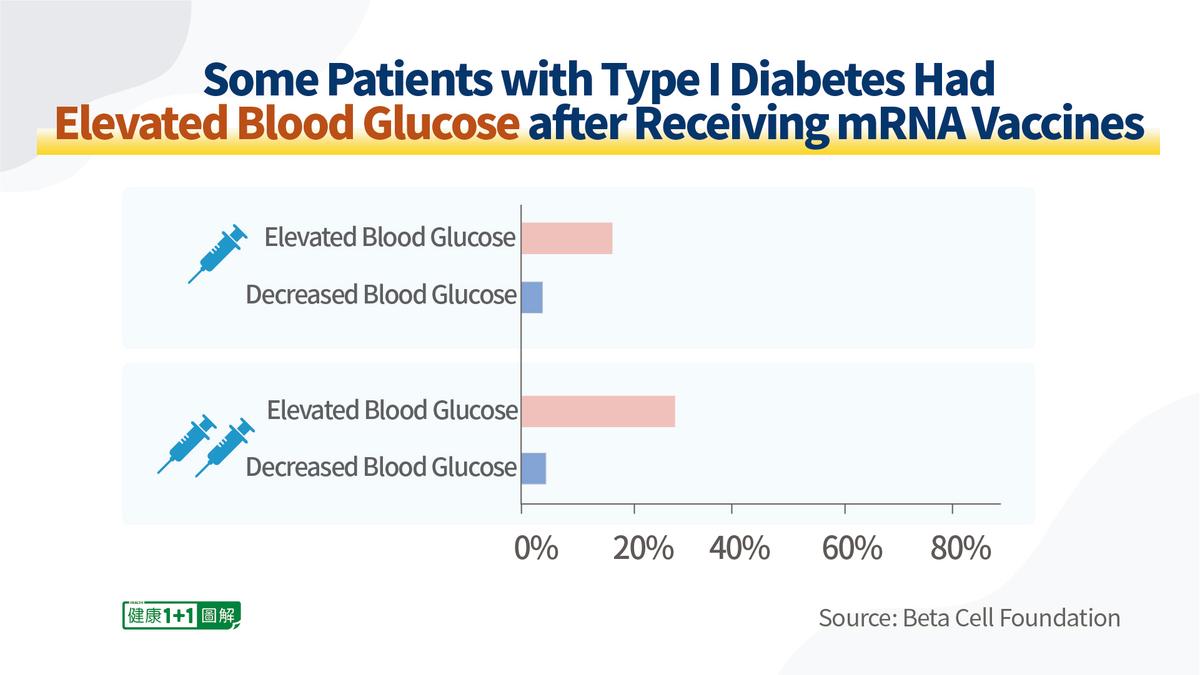
- After receiving the first dose of an mRNA vaccine (Moderna or Pfizer COVID vaccines), approximately 10 percent to 15 percent of the patients reported an increase in blood glucose within 1 to 2 days and 2 percent reported a decrease;
- After receiving the second dose of an mRNA vaccine, approximately 30 percent reported an increase in blood glucose, and 1 percent reported a decrease.
- After the second dose of the Johnson & Johnson (Janssen) vaccine, 42 percent had elevated blood glucose.







