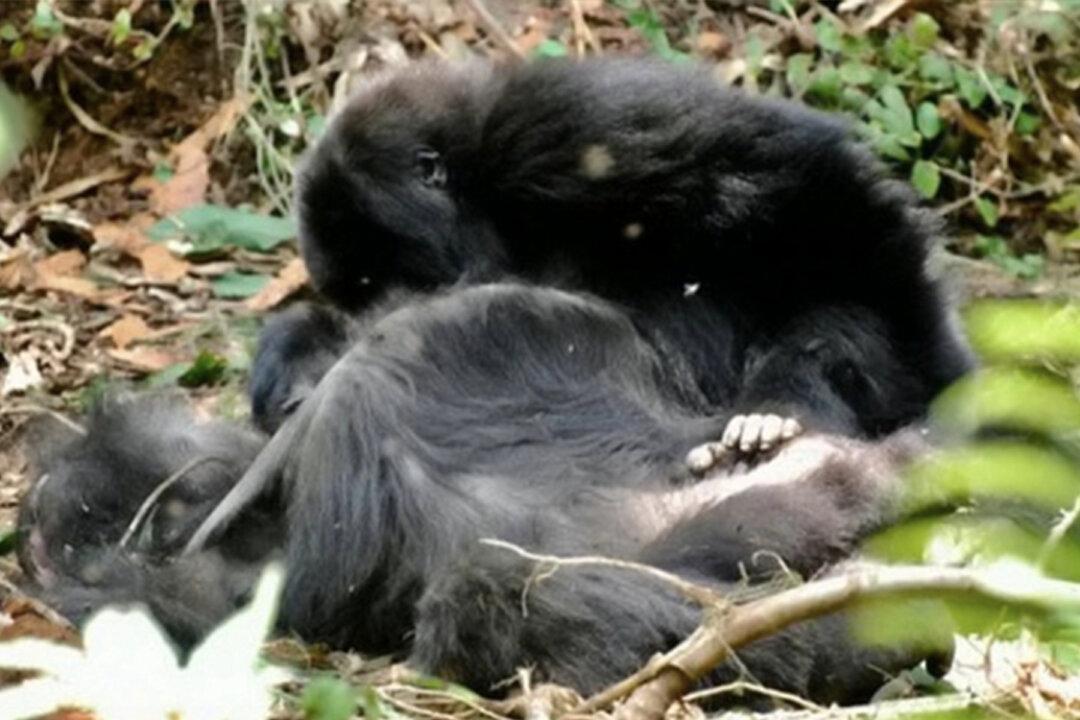
Gorillas grieve their dead and have funerals for them just like humans, according to scientists.
Their macabre rituals were the subject of a study that was published on April 2, 2019, as experts worried that their prodding and licking of corpses may spread diseases like Ebola.