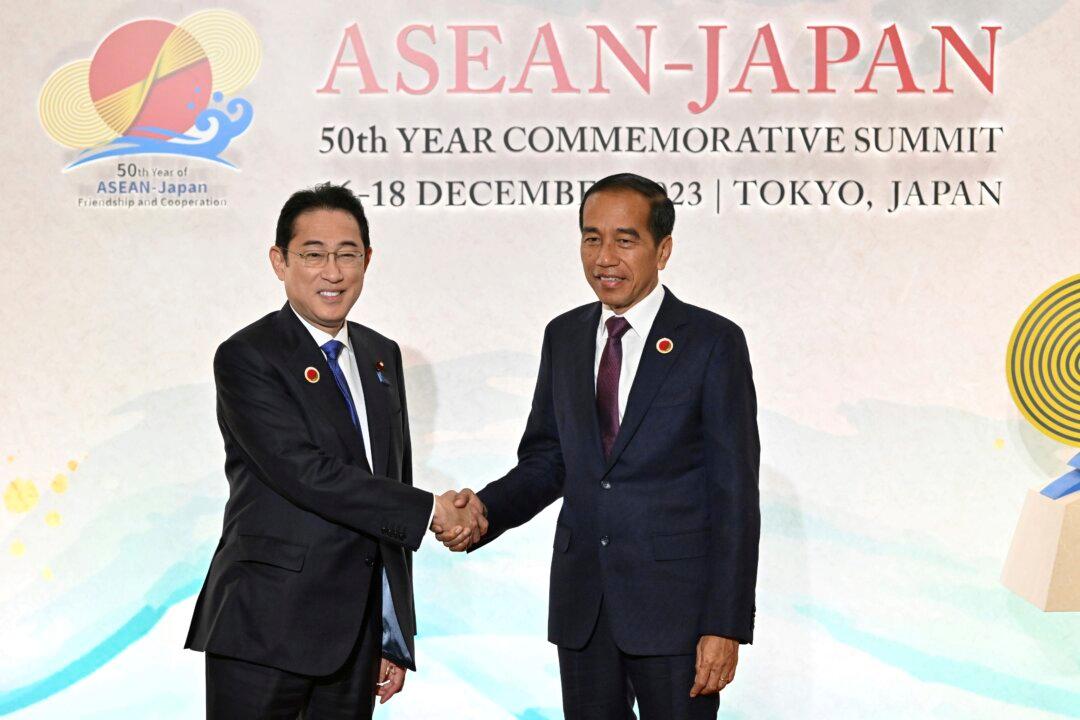
TOKYO—Leaders from Japan and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), at a special summit in Tokyo on Sunday, adopted a joint vision that emphasizes security and economic cooperation while respecting the rule of law, amid growing tensions with China in regional seas.
Ties between Japan and the 10-member ASEAN bloc used to be largely based on Japanese assistance to the developing economies, in part due to lingering bitterness over Japan’s wartime actions. But in recent years the relationship has focused more on security amid the Chinese communist regime’s growing aggressiveness in the South China Sea, while Japan’s postwar pacifist stance and trust-building efforts have fostered friendlier relations.