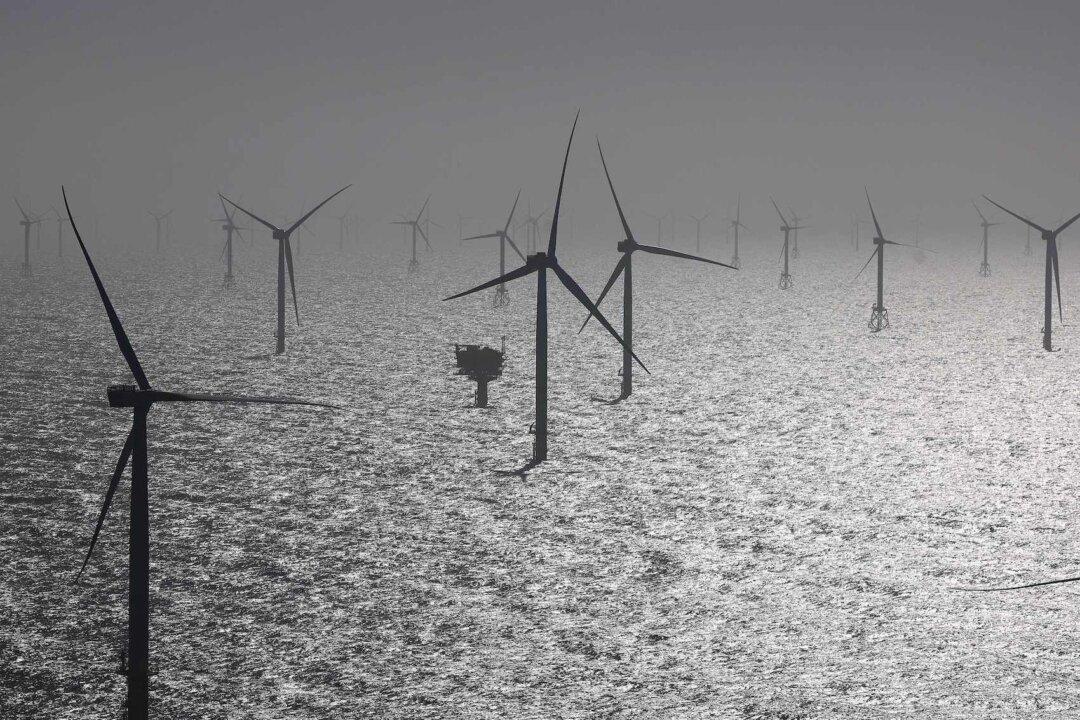
European nations’ model of tapping into one another’s electricity supplies, as many aim for ambitious net zero goals, is starting to unravel, according to some energy analysts.
A lack of wind in renewable-reliant Germany in January caused wholesale electricity prices in Norway to spike, sparking a political crisis that resulted in the collapse of the Norwegian government.