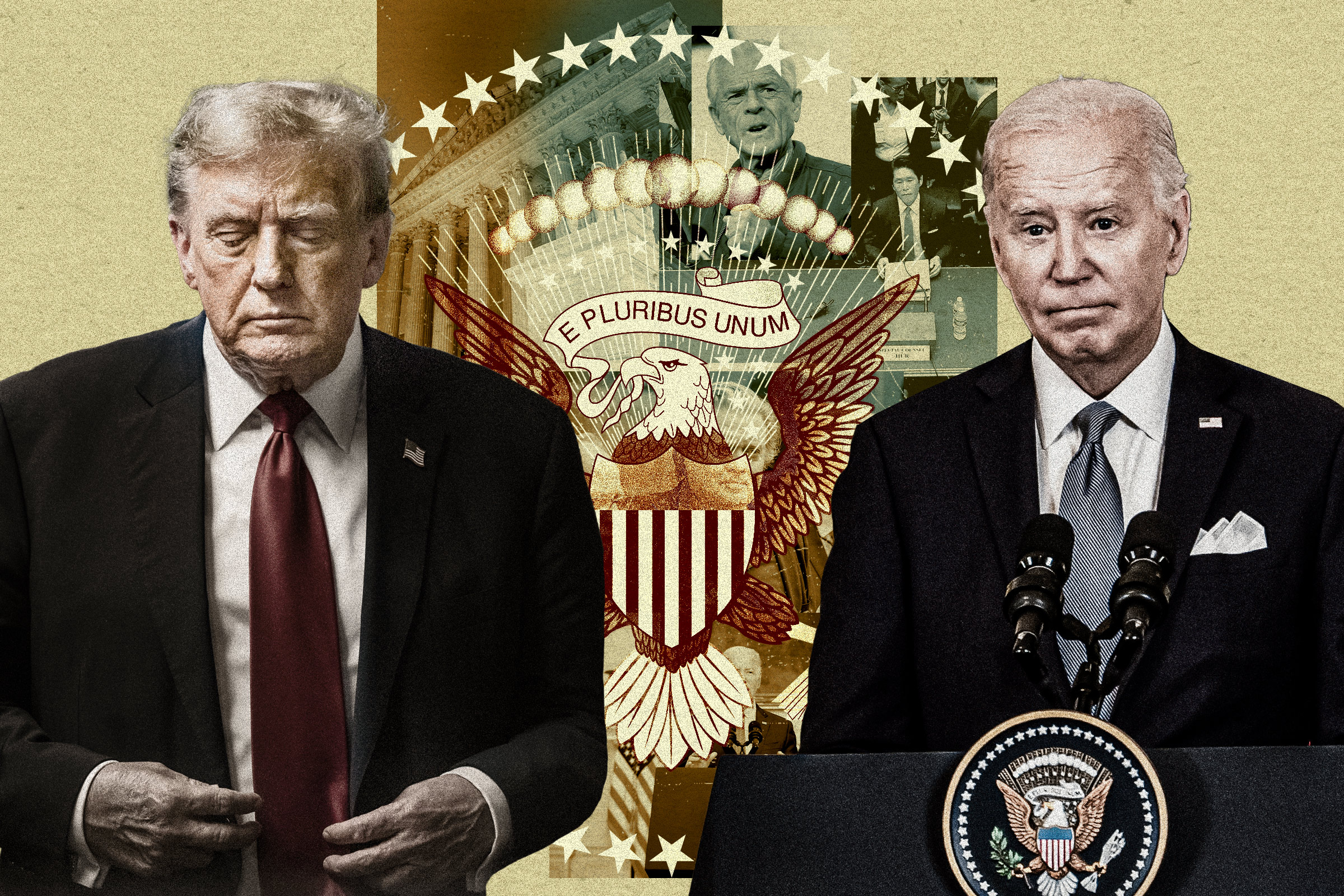
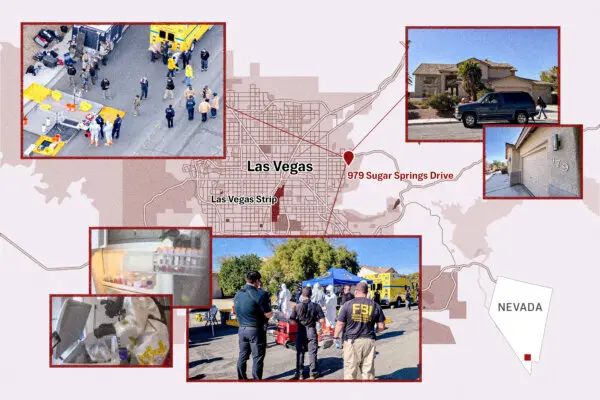
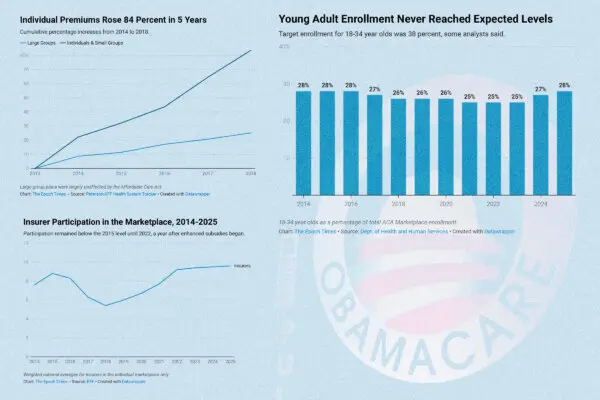
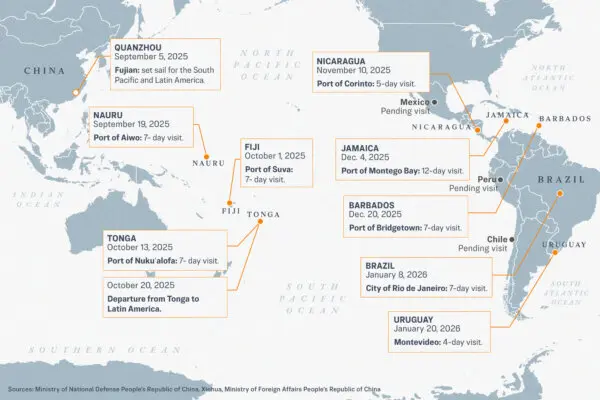
The 2024 election cycle has resurfaced longstanding debates over presidential power and how much independence the executive enjoys from other branches of government.
Executive privilege, which refers to presidents’ withholding communications from other branches, has come under scrutiny with issues surrounding both President Joe Biden and former President Donald Trump. The idea behind executive privilege is that presidents should have the freedom to speak with advisers without fear of retaliation over the content of their comments.