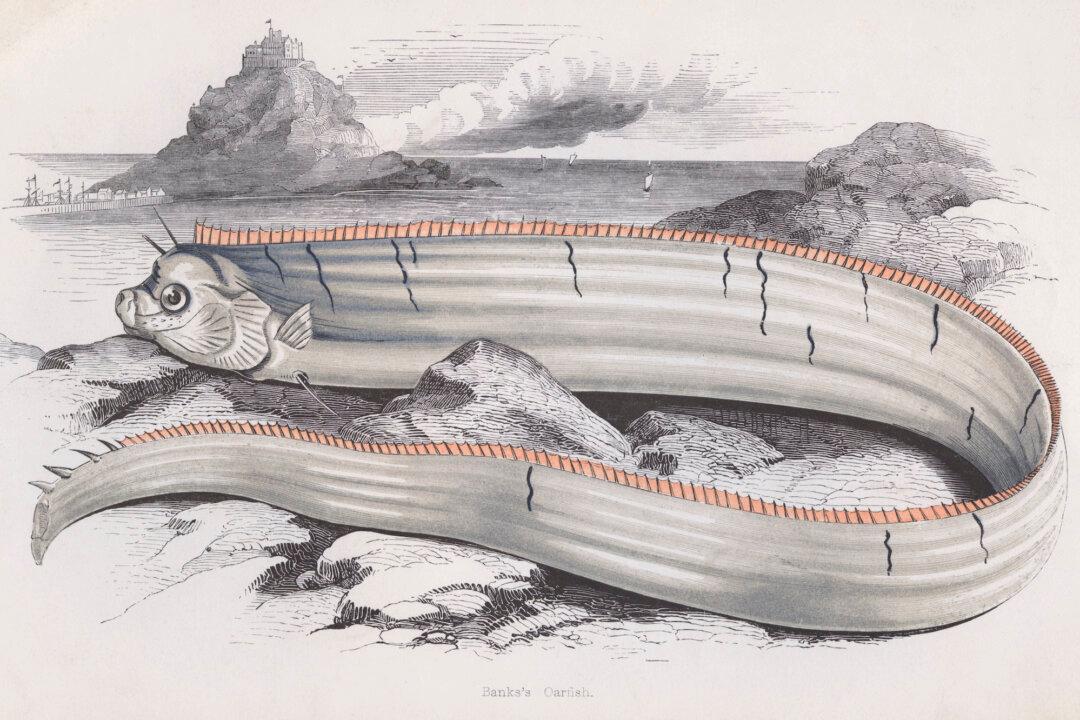
A deep-sea fish said to be a harbinger of earthquakes and tsunamis has stirred up fears in Japan after a number were recently washed ashore.
The oarfish, which can reach over 30 feet in length, is thought to be behind some of the sea serpent myths of the west.