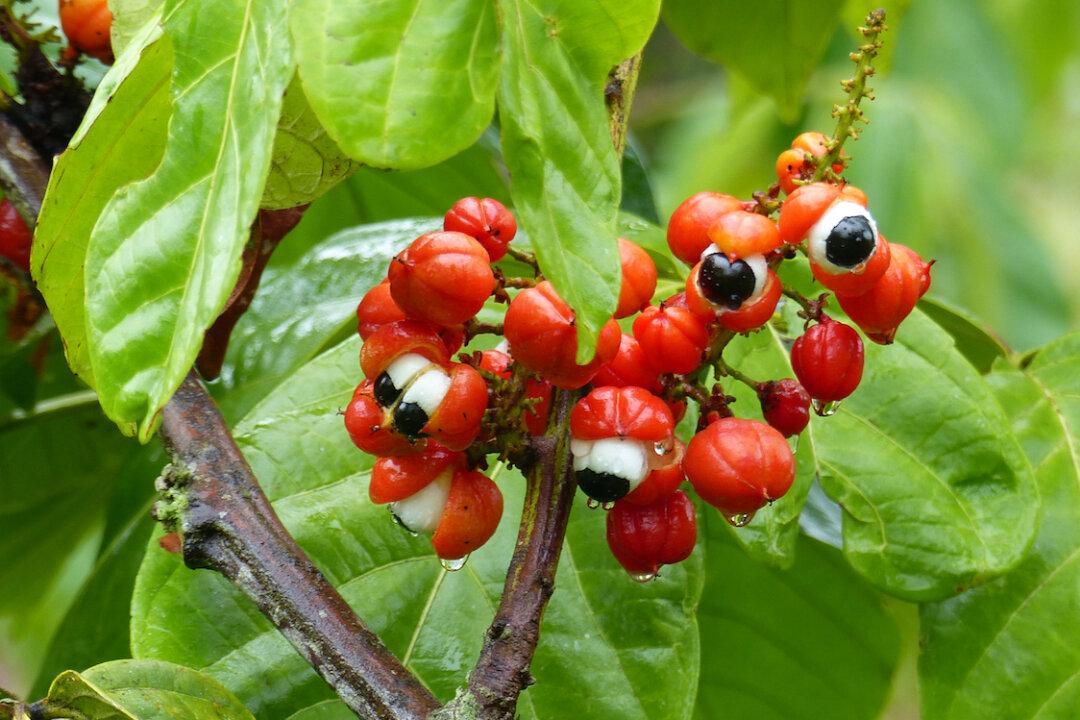
If you enjoyed an energy drink recently, chances are it contained an ingredient known as guarana (Paullinia cupana). This plant, which is native to the Amazon rainforest, is the source of a substance associated with several health benefits, along with some cautionary notes.
Guarana is a Brazilian plant highly regarded by natives for its healing qualities. The mature fruit of this climbing vine is bright red and the size of a coffee berry. The black seed in the berries is a significant source of the stimulants of caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline, as well as the antioxidants of catechin, saponin, and tannin.