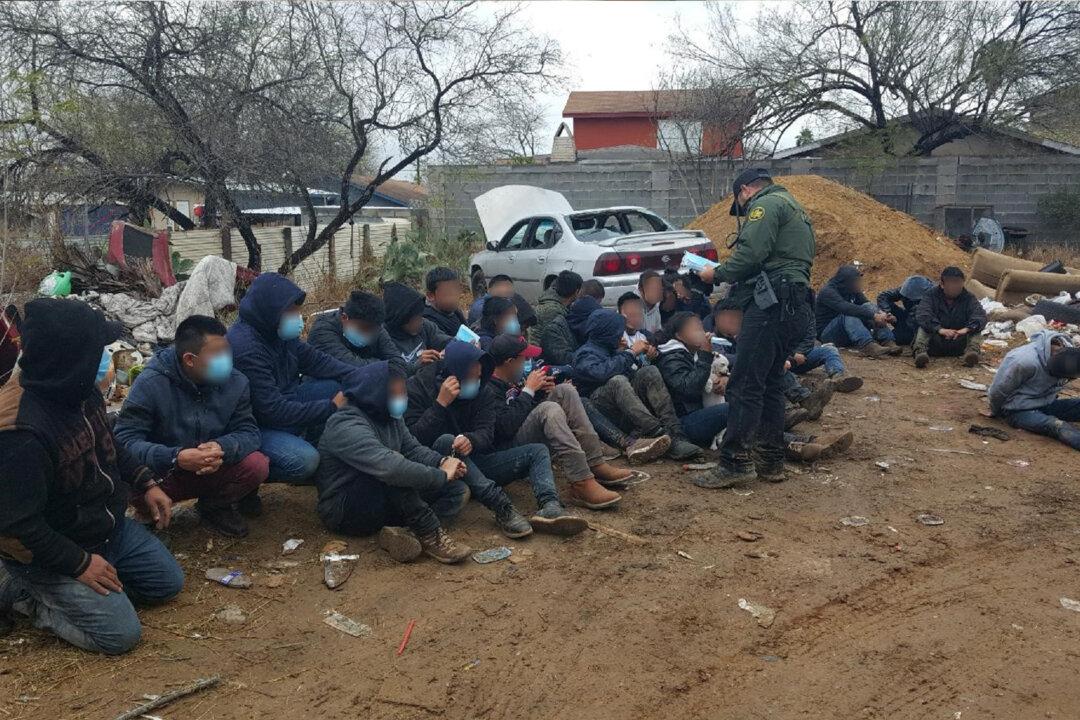
As caravans build up in Honduras, migrants are increasing at a “concerning rate” at the United States southern border, according to Matthew Hudak, U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) chief patrol agent of the Laredo sector in Texas. He warns that immigration is just a piece of the threat coupled with the pandemic health risk and other crimes along the border.
“Like everybody, we’re tracking the formation of these caravans in Central America,” said Hudak. The Laredo Sector is one of nine CBP sectors along the southern border. It contains about 135 miles of the international border with Mexico.