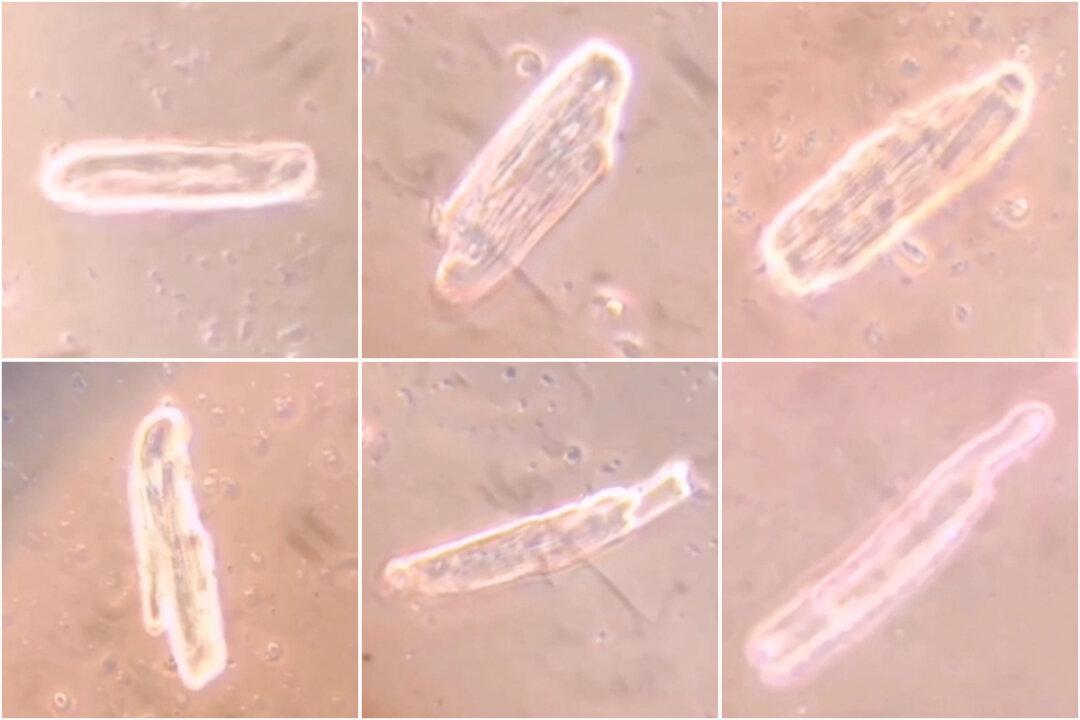
New research out of Germany observing rat and human heart cells shows that within 48 hours of vaccination, the COVID-19 mRNA vaccines form spike proteins.
Spike proteins, made from the mRNA instructions inside the vaccines, were detected in the heart cells. While both Pfizer and Moderna vaccines caused cell abnormalities, the two induced different anomalies.