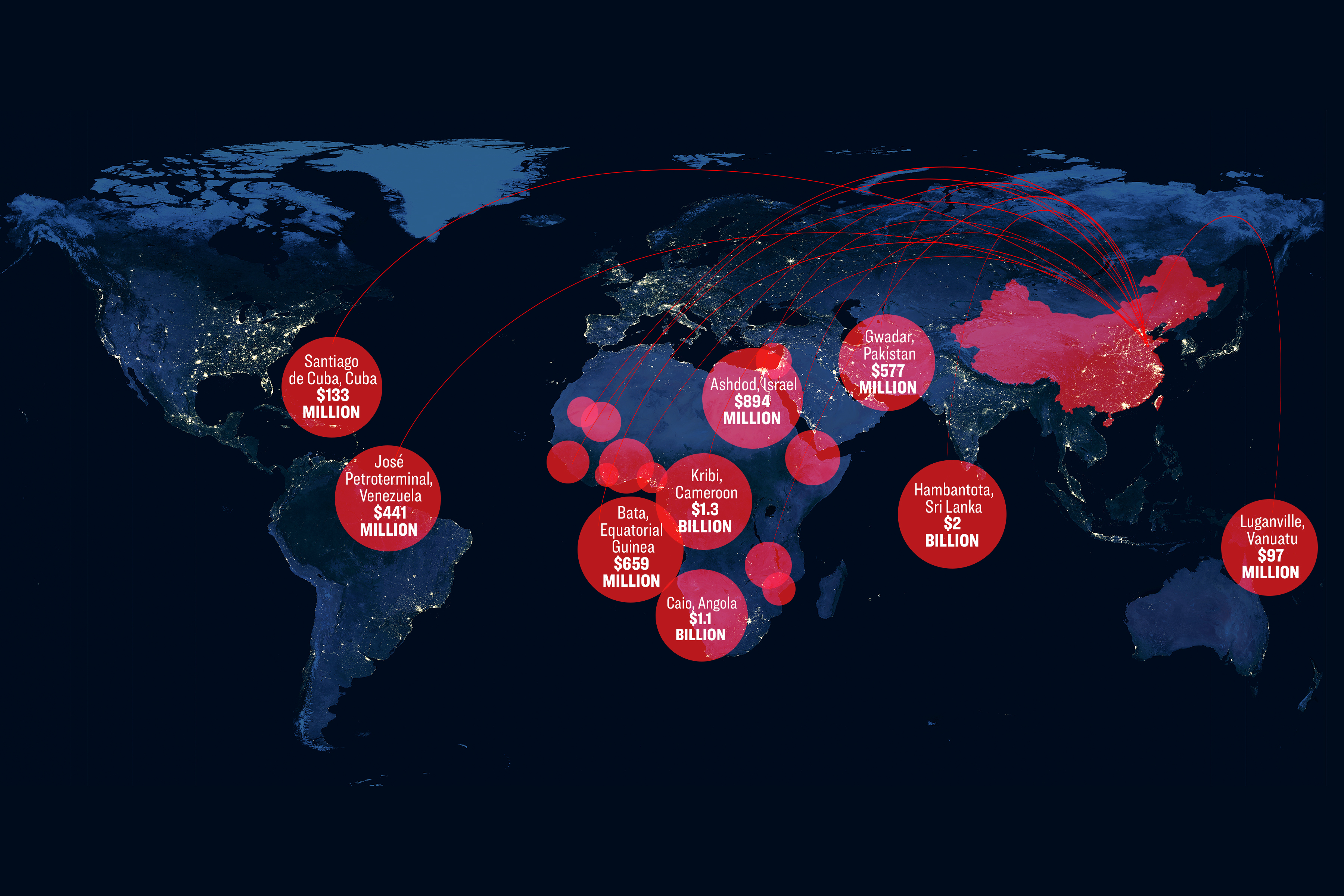
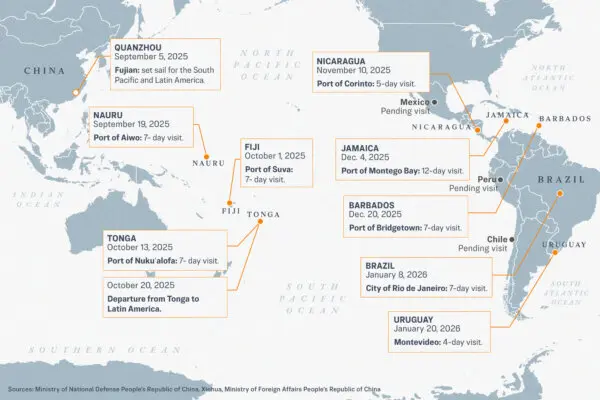
For two decades, China’s communist regime has poured tens of billions of dollars into low- and middle-income nations, funding massive port projects in the name of global development.
However, experts and lawmakers are warning that the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), which rules China as a single-party state, seeks to expand its global military presence by creating new overseas naval bases out of the commercial ports it has funded and built abroad.