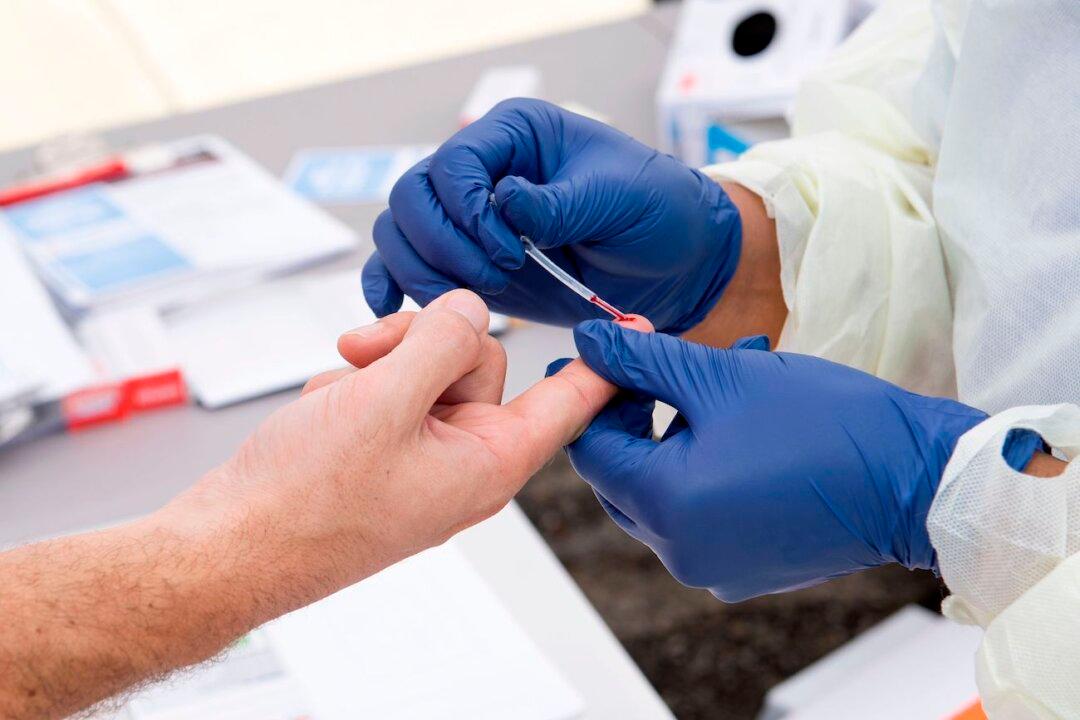
People who recover from the CCP virus develop antibodies to the disease, antibodies that determine a person’s future immunity to the disease, but a new study says that immunity may be lost within months.
The study, published July 11 (pdf), was conducted by health care workers at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ National Health Service Foundation Trust in London. They studied immune response in patients and found that the antibodies to COVID-19—the disease caused by the CCP (Chinese Communist Party) virus—decreased within a number of weeks after the onset of symptoms.