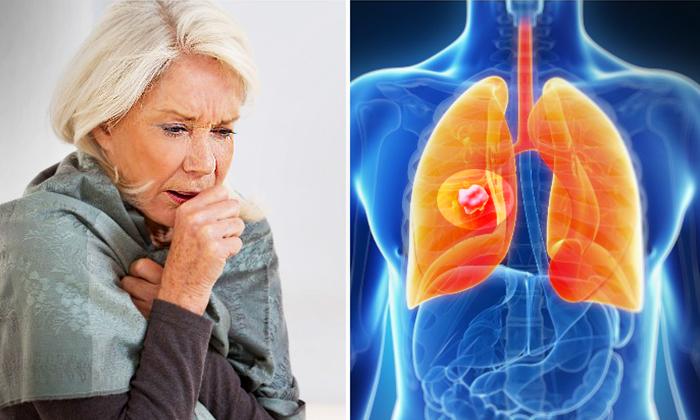
Of all types of cancer worldwide, lung cancer is the most common, accounting for about 13% of all new cancer cases. It is also the leading cause of cancer death, exceeding that of colon, prostate, and breast cancers combined. In 2018 alone, there were 2.1 million new cases of lung cancer, which caused over 1.8 million deaths, according to the World Health Organization. Statistics from the United States show similar findings, with approximately 154,050 deaths in 2018.
Although anyone can develop lung cancer, it is most prevalent in older people. The majority of those diagnosed with the disease are aged 65 or older, with the average age being 70 at the time of diagnosis. On average, men have a 1 in 15 chance of developing lung cancer in their lifetime, while women have a 1 in 17 chance.