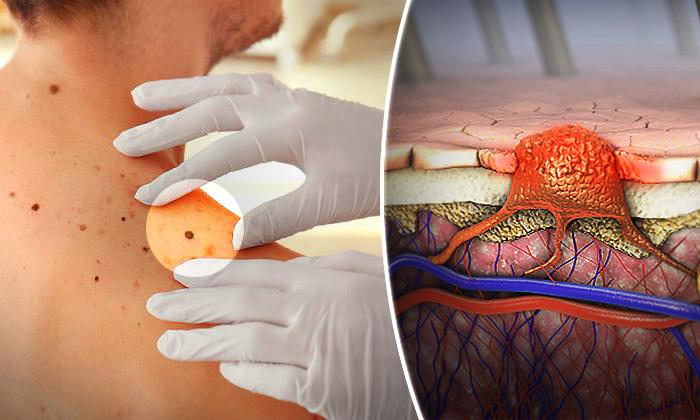
Melanoma is the most severe form of skin cancer, and it occurs in the cells responsible for producing melanin (melanocytes). Although it primarily affects the skin, it is also known to form in the eyes and, in some cases, the intestines.
According to estimates by the American Cancer Society for the United States in 2019, there will be approximately 96,480 new cases of melanoma, and about 7,230 deaths are expected to occur due to the disease. Globally, there were about 287,723 new cases of melanoma cancer diagnosed in 2018, according to the World Cancer Research Fund.